Chap 4 Review 4.2 - Network Media
4.2.1 Copper Cabling
Copper Cabling is inexpensive, easy to install and has low resistance to electrical current, but is limited by distance and signal interference.
What is Signal Attenuation?
What are the 2 sources of interference that can distort an electrical pulse?
Define EMI and RFI. What is Crosstalk?
How can electronic noise on a copper cable be limited?
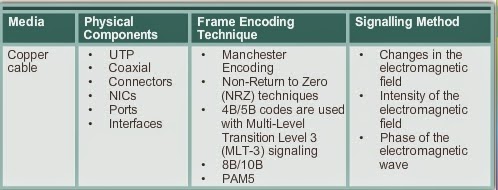
There are 3 main types of copper media:
- 4.2.1.3 Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) terminated with RJ-45
- 4.2.1.4 Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) terminated with RJ-45
How does it differ from UTP
What are the 2 common variations
It's popularity declined with the decline of Token Ring networks, but the 10GB Ethernet standard has renewed interest in it.
Although UTP has essentially replaced coax, which 2 installation types have adapted for its use?
4.2.1.6 What are the fire and electrical hazards associated with copper cable?
List some best practices to avoid these hazards.
4.2.2 - UTP Cabling
4.2.2.1 Review UTP specs: # of pairs, color-coding, twisting, wire gauge,.....
UTP does not use shielding. How is the negative effect of crosstalk limited?
What is Cancellation?
How does varying the # of twist per wire pair enhance cancellation?
4.2.2.2 What are some of the elements defined by the TIA/EIA-568A standard?
What distinguishes the difference between CAT 5 and CAT6 cable
4.2.2.3/4 Know the pin outs for straight through and crossover cables.
Identify a properly terminated cable and a cable with a bad connector.
When is straight through, crossover or rollover used?
4.2.3 Fiber Optic
How are bits encoded on a fiber optic cable?
Is fiber optic cable susceptible to EMI and RFI?
How is fiber optic used in the following industries:
- Enterprise Networks
- FTTH and Access Networks
- Long-Haul Networks
- Submarine Networks
4.2.3.2 - Identify and describe the components of a fiber cable.
Optical fiber is proof tested through a rigorous manufacturing process
for strength at a minimum of 100,000 pounds per square inch.
Taking a break - Will link in a couple worksheets comparing multi and single mode fiber, and different connectors