Tuesday, September 8, 2015
Monday, June 8, 2015
ITE Chapter 6 Review topics
Characteristics of Hub, Bridge, Switch, Router
What is an ISR
Advantages of Cellular Connectivity
Dial up vs DSL
ISDN (BRI, PRI)
cable
physical vs logical topologies (physical layout vs how host accesses the media)
Cable / Network preventive maintenance
APIPA, local link addressing
LAN, WAN, MAN, PAN
802.11 standards
Coaxial cable
IPv6 basics - 3 parts of the address, compression
IPv4 basics - 2 parts
UDP
TCP
Ethernet (802.3, CSMA/CD)
Cat 5 Standards
Client server compared to Peer to Peer
types of network data
When is a peripheral considered a host
Troubleshoot default gateway issues
Breakdown 100Base-TX. What does each component represent
Troubleshoot NICS and data transfer rates.
OSI TCP/IP models
What is an ISR
Advantages of Cellular Connectivity
Dial up vs DSL
ISDN (BRI, PRI)
cable
physical vs logical topologies (physical layout vs how host accesses the media)
Cable / Network preventive maintenance
APIPA, local link addressing
LAN, WAN, MAN, PAN
802.11 standards
Coaxial cable
IPv6 basics - 3 parts of the address, compression
IPv4 basics - 2 parts
UDP
TCP
Ethernet (802.3, CSMA/CD)
Cat 5 Standards
Client server compared to Peer to Peer
types of network data
When is a peripheral considered a host
Troubleshoot default gateway issues
Breakdown 100Base-TX. What does each component represent
Troubleshoot NICS and data transfer rates.
OSI TCP/IP models
Monday, June 1, 2015
ITE 1 June 2015
1 June 2015 - IT Essentials Chapter 6
Today you will review OSI and TCP/IP models and wireless standards, watch a video on topologies then focus on completing chapter 6.
Learning Targets:
You will be able to:
List the layers of the OSI and TCP/IP reference models and the basic functionality of each layer.
Describe the difference between a physical and logical topology and diagram each if asked.
Know the IEEE standards for wireless networking
Intall and configure both wired and wireless network cards and routers
Configure an OS for networking
1. complete the OSI quiz on the following sites:

http://compnetworking.about.com/od/osimodel/l/aa031101a.htm
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/story.php?title=osi-model_6
2. Wireless flashcards
https://quizlet.com/Stephanie_Grover/folders/chapter-4-network-access
3. Physical vs Logical Topology video clip
Review the difference between physical and logical topologies. I have shared 2 videos presenting the information in 2 different manners.
4. Pick up with 6.8 computer to network connection completing labs and filling out the packet.
Do 6.8.2.2 worksheet
Labs: 6.2.8.4 - There are 2 wireless card in the room. Zack can help locate them - One is installed in his system. Take turns installing and uninstalling those cards. If Zack's system needs a NIC, install a wired card.Do 6.8.2.9 packet tracer while waiting for one of the wireless cards.
6.8.3 Wireless and Wired Router Configurations
Read and do labs and packet tracer activities.
One of the routers is attached to a system Paul was using. There are two more routers, new the box, on the solder station. You may use those, but ensure that they are put back at the end of the day.
Tip: Check you TCP/IPv4 properties are you using DCHP or statically assigned? Is you current address on the same subnet as the router's?
6.8.3.13 requires both a wireless NIC and a router. you will have to work in teams.
6.8.4 read, fill out packet, complete labs.
Wednesday, April 8, 2015
8 April 2015
Bring the switches to the horse shoe to complete the assigned Practicals:
Practical 1; SWITCH AND TWO COMPUTERS
Practical 2: TWO SWITCHES AND TWO COMPUTERS
You can work with partners.
If you have equipment issues, use packet tracer.
The practicals call for two commands we have not talked about yet - the logging synchronous and the no ip domain-lookup commands. Watch the video clips to learn why they are useful.
Assign the switch IP address to VLAN 1 using the following commands:
Practical 1; SWITCH AND TWO COMPUTERS
Practical 2: TWO SWITCHES AND TWO COMPUTERS
You can work with partners.
If you have equipment issues, use packet tracer.
The practicals call for two commands we have not talked about yet - the logging synchronous and the no ip domain-lookup commands. Watch the video clips to learn why they are useful.
Assign the switch IP address to VLAN 1 using the following commands:
Example:
interface
Vlan1
description
Switch Telnet Connection (Answer
may vary)
ip
address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
no
shutdown
Friday, March 27, 2015
ITN Chapter 6 Review Questions
Chapter 6 Review Questions
How does a remote end acknowledge receipt of a connectionless protocol?
IPv4 fields and their purposes
IPv6 fields and their purposes
How does IPv6 handle NAT?
What are the two ways a host can display routing table
How do router forward traffic
Cisco routers: Know the iOS load sequence and where the files reside. How does this affect configuration files during an unexpected shut down. (which are lost)
Types of memory and their function
Configure a VTY interface
Why would a router boot from an iOS copy stored in ROM
What is the purpose of copy run start
What commands are used to secure a console connection
Interfaces: How do you activate an interface, then ensure that it is operational
Show commands
How would you ensure that your RAM and flash memory can support an upgrade?
How does a remote end acknowledge receipt of a connectionless protocol?
IPv4 fields and their purposes
IPv6 fields and their purposes
How does IPv6 handle NAT?
What are the two ways a host can display routing table
How do router forward traffic
Cisco routers: Know the iOS load sequence and where the files reside. How does this affect configuration files during an unexpected shut down. (which are lost)
Types of memory and their function
Configure a VTY interface
Why would a router boot from an iOS copy stored in ROM
What is the purpose of copy run start
What commands are used to secure a console connection
Interfaces: How do you activate an interface, then ensure that it is operational
Show commands
How would you ensure that your RAM and flash memory can support an upgrade?
Friday, March 6, 2015
Layer 3 Switching Chapter 5
A couple of links to help explain layer 3 switcihing
http://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/tip/Layer-3-switches-explained
https://kb.meraki.com/knowledge_base/layer-3-versus-layer-2-switch-for-vlans
http://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/tip/Layer-3-switches-explained
https://kb.meraki.com/knowledge_base/layer-3-versus-layer-2-switch-for-vlans
Friday, February 6, 2015
6 Feb 2015 - Chap 4 Review
Review Topics:
Which layer is responsible for encapsulation
Describe signaling
Why does the physical later use frame encoding
Through put vs goodput
copper cabling issues
cancellation
termination issues
rollover vs straight through vs cross over
fiber multi mode - full duplex
copper vs fiber
wireless concerns when designing a network
802.11 standards
data link's job
sending frames - start and stop bits
physical vs logical topologies
802.11 - CSMA/CA
CSMA/CD
purpose of FCS
Data Link sublayers
Test has been activated.
6 Feb 2015 CCNA - Chapter 4: 4.4 Media Access Control
4.4 Media Access Control
4.4.1.1
The Media Access Control sublayer determines how data frames are put on the media.
The actual media access control method depends on;
Topology - the connection between nodes
Media Sharing - how the nodes share the media - Point to Point (WAN) or LAN
4.4.1.2 / 4.4.3.1
Review the difference between physical and logical topologies
4.4.2.1
Common WAN topologies: Point to Point, Hub and Spoke, Mesh4.4.2.2
Physical Point to Point directly connects 2 nodes (the serial connection between routers)
4.4.2.3
In a logical Point to Point a virtual (logical) connection is made between the nodes, but the physical connection may contain intermediary devices.
4.4.2.4
Data can flow using either Half or Full Duplex communication in a point to point topology
4.4.3.2 / 4.4.3.3
Logical topology is closely tied to how data is is sent and received on the network media.
There are two basic media access control methods for shared media:
- Contention-based access: All nodes compete for the use of the medium but have a plan if there are collisions. Figure 1 shows contention-based access.
CMSA/CD Wired 802.3 Eithernet
CMSA/CA Wireless 802.11
- Controlled access: Each node has its own time to use the medium. Figure 2 shows controlled access.
The data link layer protocol dictates which media access control method will provide the appropriate balance between frame control, frame protection and network overhead
New Term: non-deterministic contention based - a device can attempt to access the medial whenever it has data to send. CSMA (Carrier Sensing Media Access) prevents chaos.
CD - Collision Detection listens for the presence of a data signal. No signal - it sends.
CA - Collision Avoidance listens for the presence of a data signal. No signal - sends an notificaiton of intent to send. Once it receives a clear to transmit, it sends the data.
4.4.3.5
Controlled access method - devices take turns to access the medium.
Token Ring (IEEE 802.5)
Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FFDI)
Both now obsolete
Review the Ring Topology and do Activity 4.4.3.7
4.4.4 Data Link Frame
Please Read the Section
A Data Link Frame has 3 basic parts: Header, Data and Trailer
But they are formatted differently depending on the protocol used: Ethernet, PPP or 802.11
Complete Activity 4.4.4.9
Wednesday, January 28, 2015
28 Jan 15 - CCNA 4.3
4.3.1 Purpose of the Data Link Layer
The Data Link Layer is responsible for the exchange of frames between nodes over a physical network media.It performs two specific services:
- Accepts Layer 3 packets and packages them into frames
- Controls media access control and performs error detection
Logical Link Control (LLC)
Media Access Control (MAC)
Watch this. It concisely explains 4.3.1.2 -4.3.1.4
28 Jan 2015 - Fiber Optic and Wireless
Fiber Optics
Please follow the link to the quizlet review for 4.2.3 coveringTypes of Fiber
Fiber Connectors
Fiber Cables
Fiber Optic Cabling Review - Quizlet
UTP Versus Fiber
Wireless Media
Wireless is not restricted to conductors or pathways and provides great mobility. However, it does have some concerns when designing a network:Coverage Area
Interference
Security
4.2.4.2 - Types of Wireless Media
Quizlet Review on Standards:
IEEE 802.11 standards Review
Do:
Lab 4.2.4. Packet Tracer - Connecting a Wired and Wireless LAN
Email Screenshot to s.grover@msad17.org
Lab 4.2.4.6 Viewing Wired and Wireless NIC Information.
Email Screenshot to s.grover@msad17.orgre
Tuesday, January 27, 2015
27 Jan 15 - CCNA Chap 4 Review 4.2
Chap 4 Review 4.2 - Network Media
4.2.1 Copper Cabling
Copper Cabling is inexpensive, easy to install and has low resistance to electrical current, but is limited by distance and signal interference.
What is Signal Attenuation?
What are the 2 sources of interference that can distort an electrical pulse?
Define EMI and RFI. What is Crosstalk?
How can electronic noise on a copper cable be limited?
There are 3 main types of copper media:
What are the 2 common variations
It's popularity declined with the decline of Token Ring networks, but the 10GB Ethernet standard has renewed interest in it.
Although UTP has essentially replaced coax, which 2 installation types have adapted for its use?
4.2.1.6 What are the fire and electrical hazards associated with copper cable?
List some best practices to avoid these hazards.
4.2.2 - UTP Cabling
4.2.2.1 Review UTP specs: # of pairs, color-coding, twisting, wire gauge,.....
UTP does not use shielding. How is the negative effect of crosstalk limited?
What is Cancellation?
How does varying the # of twist per wire pair enhance cancellation?
4.2.2.2 What are some of the elements defined by the TIA/EIA-568A standard?
What distinguishes the difference between CAT 5 and CAT6 cable
4.2.2.3/4 Know the pin outs for straight through and crossover cables.
Identify a properly terminated cable and a cable with a bad connector.
When is straight through, crossover or rollover used?
4.2.3 Fiber Optic
How are bits encoded on a fiber optic cable?
Is fiber optic cable susceptible to EMI and RFI?
How is fiber optic used in the following industries:
Optical fiber is proof tested through a rigorous manufacturing process for strength at a minimum of 100,000 pounds per square inch.
Taking a break - Will link in a couple worksheets comparing multi and single mode fiber, and different connectors
4.2.1 Copper Cabling
Copper Cabling is inexpensive, easy to install and has low resistance to electrical current, but is limited by distance and signal interference.
What is Signal Attenuation?
What are the 2 sources of interference that can distort an electrical pulse?
Define EMI and RFI. What is Crosstalk?
How can electronic noise on a copper cable be limited?
There are 3 main types of copper media:
- 4.2.1.3 Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) terminated with RJ-45
- 4.2.1.4 Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) terminated with RJ-45
What are the 2 common variations
It's popularity declined with the decline of Token Ring networks, but the 10GB Ethernet standard has renewed interest in it.
- 4.2.1.5 Coaxial Cable
Although UTP has essentially replaced coax, which 2 installation types have adapted for its use?
4.2.1.6 What are the fire and electrical hazards associated with copper cable?
List some best practices to avoid these hazards.
4.2.2 - UTP Cabling
4.2.2.1 Review UTP specs: # of pairs, color-coding, twisting, wire gauge,.....
UTP does not use shielding. How is the negative effect of crosstalk limited?
What is Cancellation?
How does varying the # of twist per wire pair enhance cancellation?
4.2.2.2 What are some of the elements defined by the TIA/EIA-568A standard?
What distinguishes the difference between CAT 5 and CAT6 cable
4.2.2.3/4 Know the pin outs for straight through and crossover cables.
Identify a properly terminated cable and a cable with a bad connector.
When is straight through, crossover or rollover used?
4.2.3 Fiber Optic
How are bits encoded on a fiber optic cable?
Is fiber optic cable susceptible to EMI and RFI?
How is fiber optic used in the following industries:
- Enterprise Networks
- FTTH and Access Networks
- Long-Haul Networks
- Submarine Networks
Optical fiber is proof tested through a rigorous manufacturing process for strength at a minimum of 100,000 pounds per square inch.
Taking a break - Will link in a couple worksheets comparing multi and single mode fiber, and different connectors
4 March 2015 - CCNA Chap 4 Review 4.1
Chapter 4 - Network Access 4.1 Physical Layer Protocols
Review
4.0.1.1 -
Terms related to the physical or wireless connection to a network: WAP. ISR, LAN, NIC, WLAN
4.1.2
The OSI physical layer provides the means to transport the bits that make up a data link later frame across the network media.
What is the process that data undergoes from source node to destination?
Review the PDU encapsulation process
What are the 3 basic forms of network media?
4.1.3
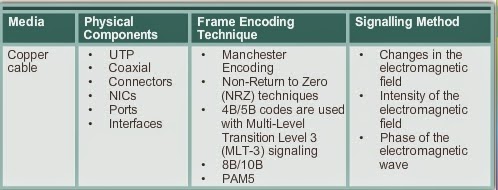
The 3 functional areas that the physical layer addresses: Physical components, Encoding and Signaling
How does throughput differ from goodput?
What is latency?
4.1.3.4 What role do standards play in defining media?
DO: 4.1.3.5
Review
4.0.1.1 -
- Which 2 layers of the OSI model are so closely tied that the TCP/IP combines them into one layer?
- What is the role of the data link layer on the sending device? What does it do on the receiving device?
Terms related to the physical or wireless connection to a network: WAP. ISR, LAN, NIC, WLAN
4.1.2
The OSI physical layer provides the means to transport the bits that make up a data link later frame across the network media.
What is the process that data undergoes from source node to destination?
Review the PDU encapsulation process
What are the 3 basic forms of network media?
4.1.3
The 3 functional areas that the physical layer addresses: Physical components, Encoding and Signaling
Define Encoding
Signaling:
- What is the difference between Asynchronous and Synchronous signal transmission?
- What are the 3 commonly used modulation techniques?
How does throughput differ from goodput?
What is latency?
4.1.3.4 What role do standards play in defining media?
DO: 4.1.3.5
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)